Scurvy, caused by vitamin C deficiency, has an interesting history. James Lind discovered in 1747 that only oranges and lemons could treat scurvy, a common problem among sailors. Animals can synthesize vitamin C, but Axel Holst and Theodor Frölich produced scurvy in guinea pigs. Vitamin C was identified by Charles Glen King in 1932, and Norman Haworth deduced its chemical structure in 1933 (Carpenter, 2012).
Vitamin C: Its importance, functions, and how much you need.
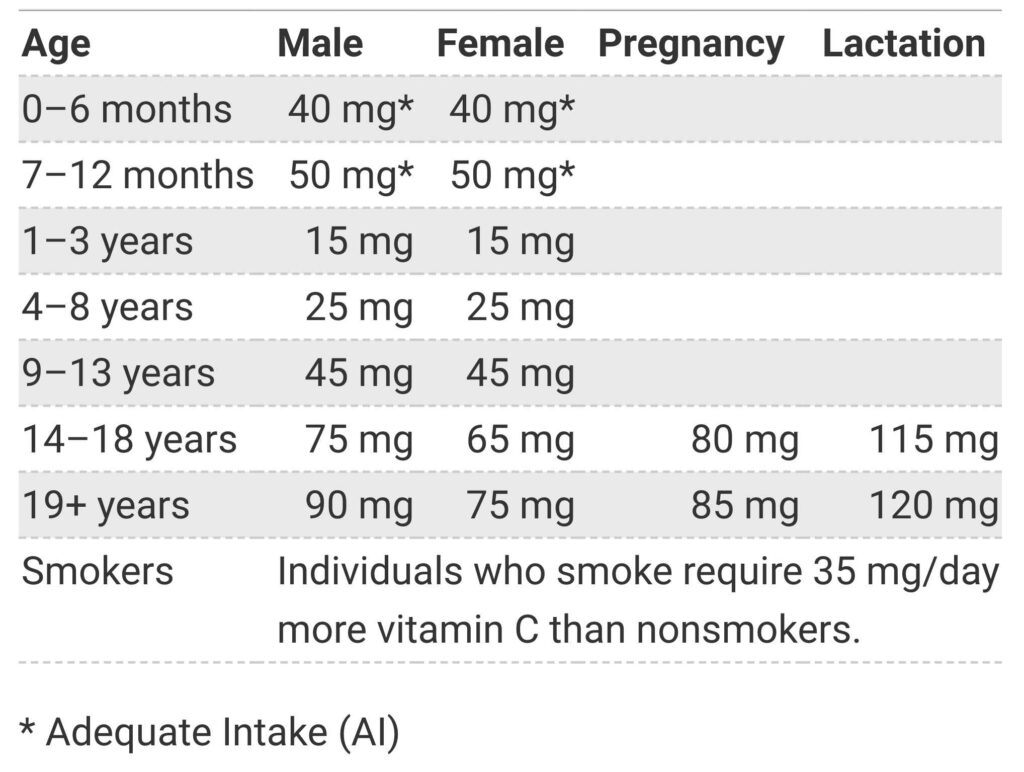
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that humans can’t synthesize (unlike most animals). It is essential for enzymatic reactions, collagen production, and gene expression regulation (Naidu, 2003). It is also a potent antioxidant (Buettner, 1993). Studies show that higher vitamin C status may lower the risks of hypertension, coronary heart disease, and stroke (Morelli et al., 2020). Vitamin C supplements are well-documented to help shorten the duration of the common cold but do not reduce the risk of becoming ill (Rondanelli et al., 2018). No scientific evidence suggests that large amounts of vitamin C in adults have adverse or toxic effects. Due to its osmotic effect, unabsorbed vitamin C in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, and other gastrointestinal disturbances (Jacob & Sotoudeh, 2002a). The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for adults aged 19 and above is 90mg daily for men and 75mg for women. However, during pregnancy and lactation periods, the vitamin C requirement increases to 85mg and 120mg per day, respectively. Therefore, a balanced diet is essential, including foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, kiwi, strawberries, broccoli, and tomatoes, to meet these daily requirements and maintain good health (Levine et al., 2001).
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for Vitamin C
1. Dry, Damaged Skin
Healthy skin contains a sizable amount of vitamin C, which helps to maintain it by shielding it from oxidative damage caused by the sun and exposure to harmful pollutants like environmental toxins (Pullar et al., 2017) (Podda et al., 1998). It also encourages the production of collagen, which keeps the skin youthful-looking (Duarte et al., 2009). Studies show that individuals with high vitamin C intake generally have better skin quality, while those with lower intake have a 10% increased risk of developing dry, wrinkled skin (Iizaka et al., 2016). However, it’s important to note that vitamin C deficiency is one of the various factors that can cause dry and damaged skin (Cosgrove et al., 2007).
2. Easy Bruising
When blood vessels beneath the skin rupture, a discoloration known as bruising occurs when blood leaks into the surrounding tissue; if you experience easy bruising, it could indicate a vitamin C deficiency (Hirschmann & Raugi, 1999a). This nutrient is essential for producing collagen, which helps keep the skin, bones, and other tissues healthy and strong. A lack of vitamin C can weaken blood vessels and cause poor collagen production, making you more susceptible to bruising (Pimentel, 2003a).
3. Slowly Healing Wounds
When our body has insufficient vitamin C, the rate of collagen formation slows down, leading to a delay in the healing process of wounds (Galimberti & Mesinkovska, 2016). Recent research suggests that people who suffer from chronic, non-healing injuries are more likely to be vitamin C deficient. In some acute cases of vitamin C deficiency, old wounds may reopen, increasing the risk of infection (Lazareth et al., 2007). Slow wound healing or reopening old wounds is an advanced sign of deficiency that can heighten the risk of infection (Fain, 2005a). Therefore, maintaining adequate levels of vitamin C in our body promotes faster wound healing and reduces the risk of infection (Hirschmann & Raugi, 1999a).
4. Bleeding and Swollen Gums
When the body lacks sufficient vitamin C, the gum tissue may become weak and inflamed, and the blood vessels may start bleeding more easily. This can lead to the gums appearing red, swollen, and bleeding (Olmedo et al., 2006). Moreover, the gums may even take on a purplish hue in severe cases of vitamin C deficiency. Unhealthy gums can also affect the integrity of teeth over a prolonged timeframe (Larralde et al., 2007) (Fain, 2005a). Therefore, ensuring adequate vitamin C intake through a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial.
5. Painful Swollen Joints
Did you know that your joints contain a lot of collagen-rich connective tissue, which can also be affected by vitamin C deficiency? You must get enough vitamin C to keep your joints healthy and functioning correctly (Tamura et al., 2000).
6. Poor Immunity
Vitamin C is essential for obtaining a healthy immune system, which may increase the risk of severe infections like pneumonia (Johnston et al., 2014). Scientific studies suggest that vitamin C accumulates inside different types of immune cells, enhancing their function and aiding them in fighting diseases and destroying harmful pathogens (Carr & Maggini, 2017).
It is worth noting that people with scurvy, a condition caused by vitamin C deficiency, often suffer from a weakened immune system. If not treated promptly, this can result in a higher susceptibility to infections and, worse, fatalities (Pimentel, 2003a). An adequate amount of vitamin C in your diet is recommended to maintain a healthy immune system.
7. Iron Deficiency Anemia
There is a notable link between vitamin C and iron deficiency anemia. Low levels of vitamin C can contribute to iron deficiency anemia by reducing iron absorption from plant-based foods and negatively affecting iron metabolism (Teucher et al., 2004) (Lane & Richardson, 2014). Additionally, vitamin C deficiency increases the risk of excessive bleeding, which can lead to anemia (Agarwal et al., 2015).
If you are experiencing iron deficiency anemia without any apparent causes, it is recommended to check your vitamin C levels.
8. Fatigue
When your body doesn’t receive enough vitamin C, it can lead to various health problems. Fatigue and a glum mood are some of the earliest signs of vitamin C deficiency (Maggini et al., 2010). These symptoms may appear before the deficiency reaches its full-blown state (Levine et al., 1996). Though fatigue and irritability are some of the first symptoms, they can often be resolved by increasing your daily vitamin C intake (Levine et al., 1996).
9. Oxidative Stress leading to Chronic Inflammation
Vitamin C is one of the most critical antioxidants, fighting cellular damage caused by free radicals. Low vitamin C intake has been shown to increase the risk of heart disease, oxidative stress, and inflammation (Helmersson et al., 2008) (Moser & Chun, 2016). A study found that people with low blood levels of vitamin C were 40% more prone to progress into heart failure within 15 years than those with high blood levels (Pfister et al., 2011).
Which foods are highest in vitamin C?
Vitamin C is essential for our body’s growth, development, and repair. Men’s recommended dietary intake (RDI) of vitamin C is 90 milligrams daily, while women require 75 milligrams daily (Jacob & Sotoudeh, 2002b). However, it’s important to note that certain factors, such as smoking, pregnancy, and illness, can increase the demand for vitamin C in the body (Jen & Yan, 2010) (Gariballa & Forster, 2009). Fortunately, plenty of delicious foods are rich in vitamin C. Some of the best sources of vitamin C include:
- Oranges
- Grapefruits
- Lemons
- Kiwi
- Strawberries
- Papaya
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Tomatoes.
- Acerola cherry
- Guava
- Blackcurrants
- Sweet red pepper, and
- Parsley
-
Incorporating these vitamin C-rich foods into your diet ensures you meet your daily requirements for this crucial nutrient.
Vitamin C taken as a Supplement
Although research on the effectiveness of vitamin C in curing the common cold has been controversial, evidence suggests that it might shorten the duration or severity of a cold (Bucher & White, 2016). However, whether vitamin C can prevent a cold is still unclear. It has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of colds but not the frequency.
Mainstream medicine has traditionally relied on eminence-based (relying on medical opinion) rather than evidence-based medicine for vitamin C and infections (Hemilä & Chalker, 2022).
Expensive Pee?
It’s not uncommon to hear critics claim that taking supplements equates to ‘expensive pee,’ implying that these supplements are a waste of money. While it’s certainly understandable to question the efficacy of supplements, it’s also important to understand that absorption plays a crucial role in determining their effectiveness. To ensure that you’re getting the most out of your investment, it’s essential to take specific steps to optimize the absorption of these supplements in your body. High-quality products should also be considered when buying any supplement.
Forms of Vitamin C Supplements
Liposomal vitamin C
Did you know that liposomal vitamin C is considered the best form of vitamin C? Most people with severe vitamin C deficiency also have a gut malabsorption problem. Liposomal vitamin C helps to address this problem and ensures that your body gets the vitamin C needed to function at its best (Gopi & Balakrishnan, 2020).
Supplements Recommendation
Natural Factors Vitamin C, 180 Tabs
This isn’t your average vitamin C. Natural Factors Vitamin C is elevated with citrus bioflavonoids and rosehips – nature’s secret to enhanced absorption – to unlock the true power of vitamin C. Working in synergy, they optimize the body’s usage of vitamin C, provide antioxidant protection, keep collagen healthy, and help support capillary strength.
New Roots Herbal Vitamin C⁸, 180 Caps
Vitamin C⁸ is a comprehensive vitamin C source containing eight forms of buffered vitamin C and additional nutraceuticals for excellent health. It combines mineral ascorbates with ascorbyl palmitate, providing a full spectrum of antioxidant benefits, boosting immune function, and replenishing electrolytes. It also delivers the antioxidant action of three cups of green tea per capsule.