Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, can be a serious and potentially deadly condition if not detected and treated early. Though prevention is key, it is also important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melanoma to ensure timely intervention. One effective method for identifying potential melanoma growths is through the ABCDE rule.
The ABCDEs: The Signs of Melanoma
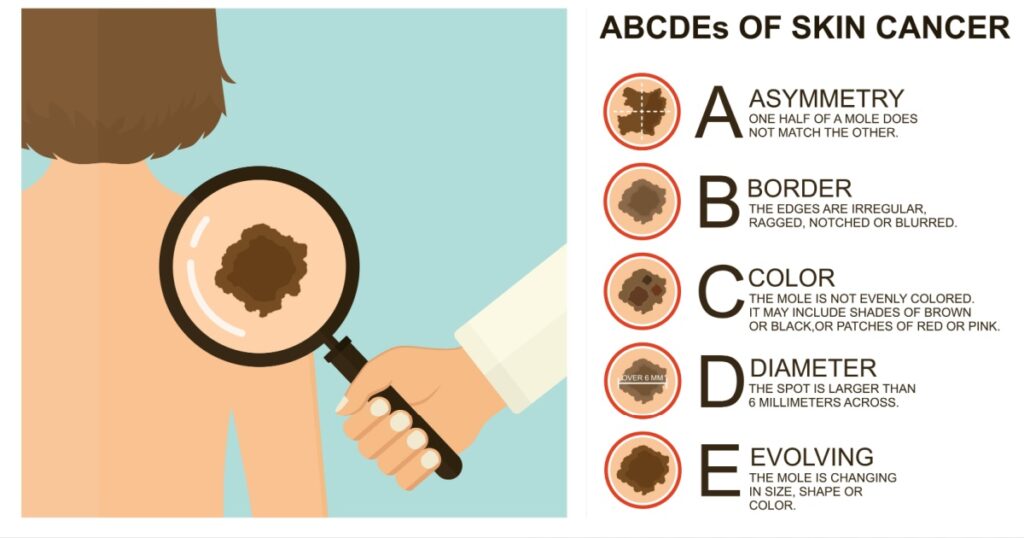
It can be tough when checking out the various moles and marks on your body to tell if they should be of concern or not. While the rule when in doubt, get it checked out is always a good idea, you may have the time or resources to see the dermatologist quite so often. The ABCDE rule is a simple way to remember which moles are concerning and which are not. This rule stands for: asymmetry, border, color, diameter, and evolving. Each one has to do with the appearance and behavior of your moles, requiring you to regularly monitor them so that you are aware of any changes that may occur. By familiarizing yourself with these characteristics, you can better recognize suspicious moles or growths on your skin that may require further evaluation by a healthcare professional. (1)
1. Asymmetry
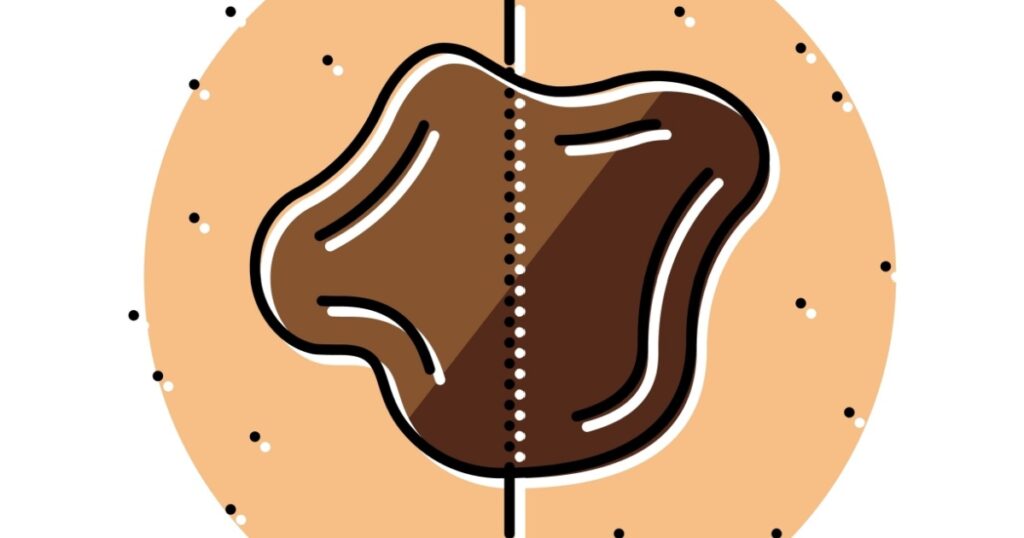

One of the key signs of melanoma is asymmetry. Most moles are more or less symmetrical, whereas cancerous ones usually are not. When examining a mole or growth, visualize it as if drawing an imaginary line cutting it in half. If one half looks different from the other half, it may be a cause for concern and should be evaluated further.
2. Border
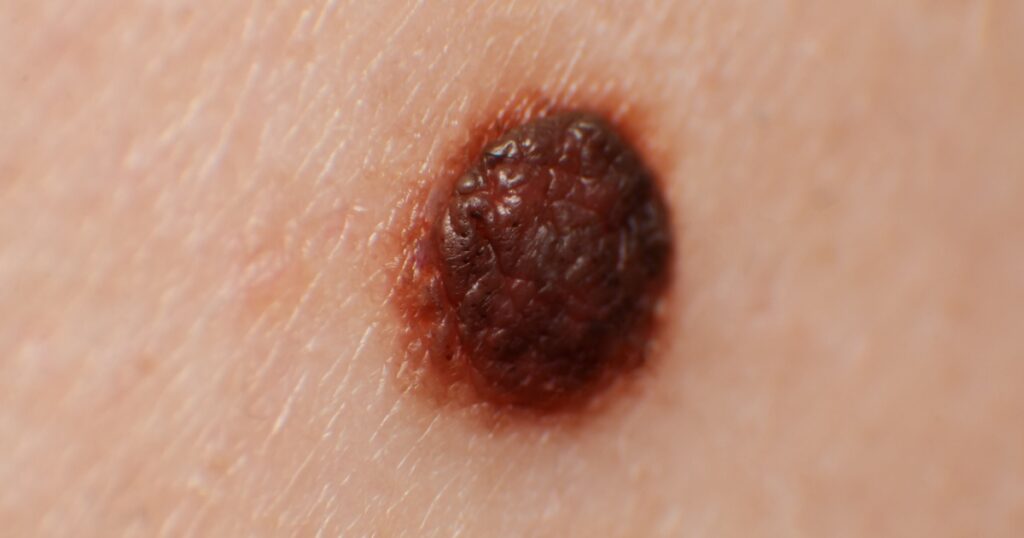
The border of a mole or growth can provide important clues about its nature. A melanoma growth often has a jagged, blurry, or uneven border. This is unlike the smooth and well-defined borders commonly associated with non-cancerous moles. Any irregularities in the border should be taken seriously and warrant medical attention.
3. Color
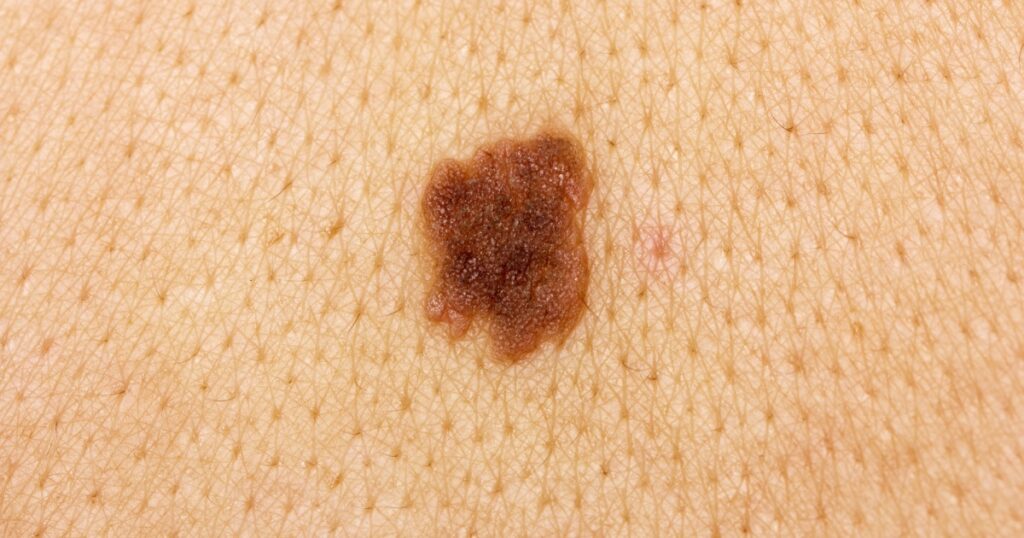
Melanoma growths can exhibit a wide range of colors. When examining a mole or growth, look for variations in color, including shades of brown, black, red, white, gray, or blue. Multiple colors within a single growth, especially if they are unevenly distributed, can be a warning sign and merit further investigation.
4. Diameter

The size of a mole or growth can also be indicative of melanoma. While not all large moles are cancerous, any growth exceeding 6 millimeters (mm) in diameter should be examined by a healthcare professional. Monitoring the evolution of the size of a mole over time is crucial, as significant growth may be a cause for concern.
5. Evolving
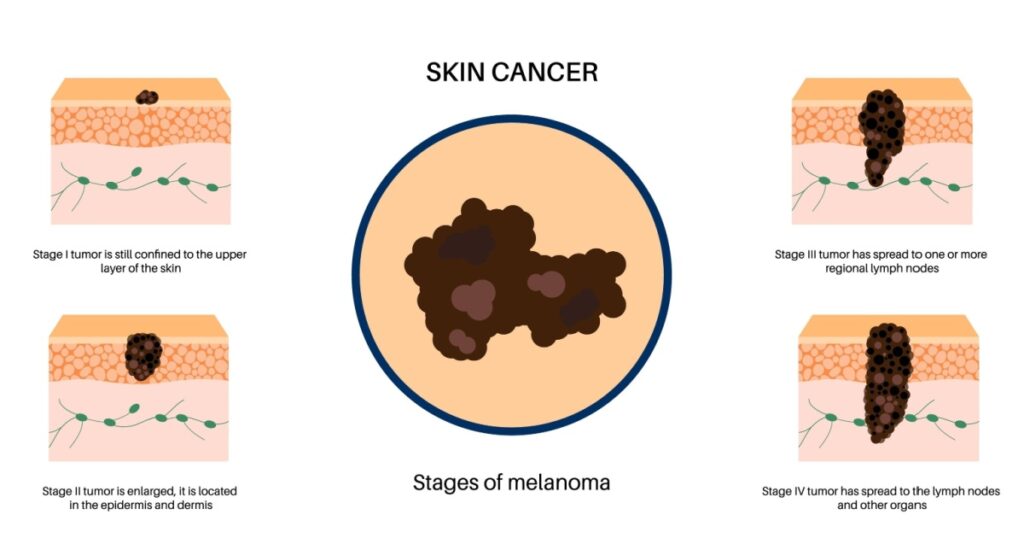
The evolution of a mole or growth is an essential characteristic to consider. Changes in size, shape, color, or texture, such as becoming scaly, lumpy, hard, itchy, or bloody, could be signs of malignancy. Regularly assess any moles or growths on your skin for these alterations, and consult a healthcare provider if you notice any significant changes.
Take Note of Other Risk Factors
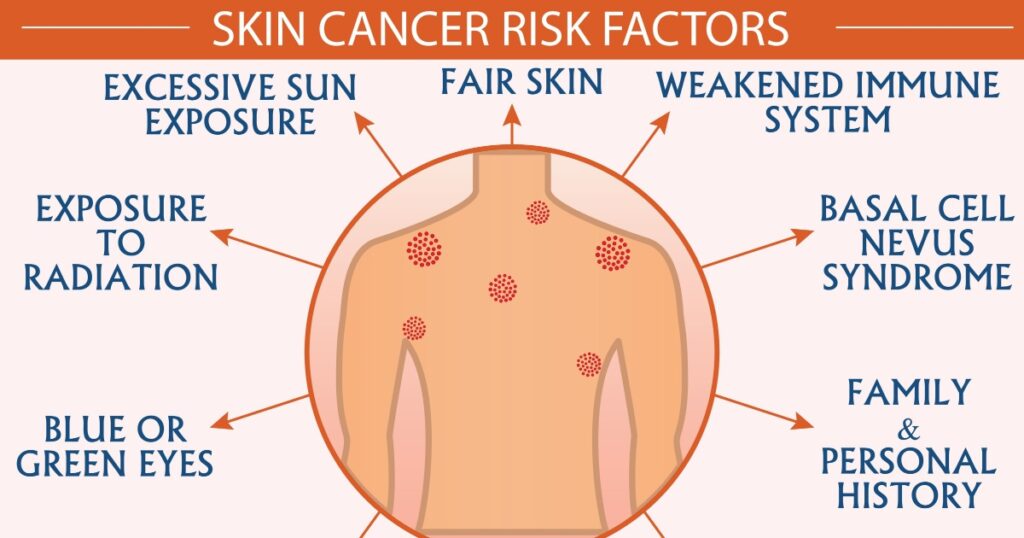
It is worth noting that melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, but it often appears on areas of the skin that have been exposed to the sun. Additionally, certain risk factors, such as a family history of melanoma, a weakened immune system, and the presence of many moles on the body, can increase the likelihood of developing melanoma. (2)
While the ABCDE rule is a useful tool for recognizing potential signs of melanoma, it is important to remember that not all cases will exhibit all of these characteristics. In some rare instances, melanoma growths may lack pigment or resemble benign tumors, making them more challenging to identify. Additionally, children and teenagers may have different presentations of melanoma that may not meet the ABCDE criteria.
Diagnosing Melanoma

Diagnosing melanoma requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, which may include tests, such as a biopsy, to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. If melanoma is detected, further treatment options, including surgical excision, immunotherapy, molecular targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, may be recommended based on the stage and severity of the cancer.
The Bottom Line
