Our skin, the body’s largest organ, serves as a reflection of our overall health. From rashes and discoloration to dryness and texture, the skin can manifest a wide range of symptoms that can indicate underlying medical conditions. Understanding these manifestations and seeking appropriate medical attention can be crucial in detecting and addressing potential health issues.
Understanding Our Skin, Our Body’s Biggest Organ

The skin is a complex and multifunctional organ that plays a vital role in protecting our body from external threats such as bacteria, viruses, and environmental factors. Comprising several layers, the skin serves as a barrier while also regulating body temperature, sensation, and providing a crucial interface with the external environment. (1) With a total area of approximately 20 square feet, the skin’s significance goes beyond its physical attributes. It also provides valuable insight into our health, often indicating the presence of systemic diseases through various visible signs and symptoms.
10 Medical Conditions Revealed Through Our Skin

Changes in our skin can often be one of the earliest indicators that something isn’t quite right with our health. This can be things like dehydration, fatigue, allergies, or nutrient deficiencies. They can also be a sign of bigger issues with our health, including autoimmune diseases and even cancer. Understanding these more is the first step towards treatment and better health.
1. Eczema
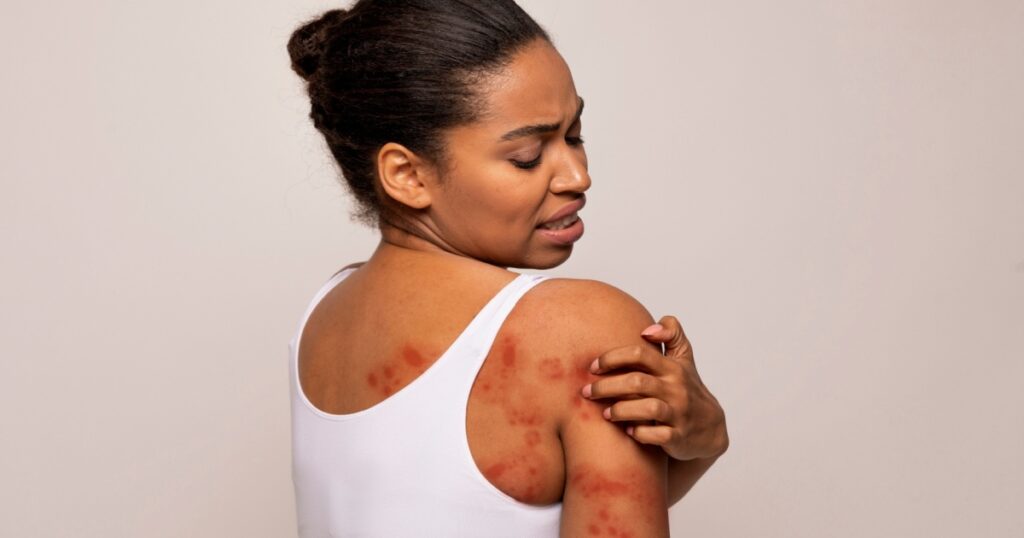
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition characterized by inflamed, itchy skin. The affected areas may develop redness, swelling, and crusting, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Managing eczema involves keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding triggers, and in severe cases, seeking medical treatment such as topical or oral medications. (2)
2. Psoriasis
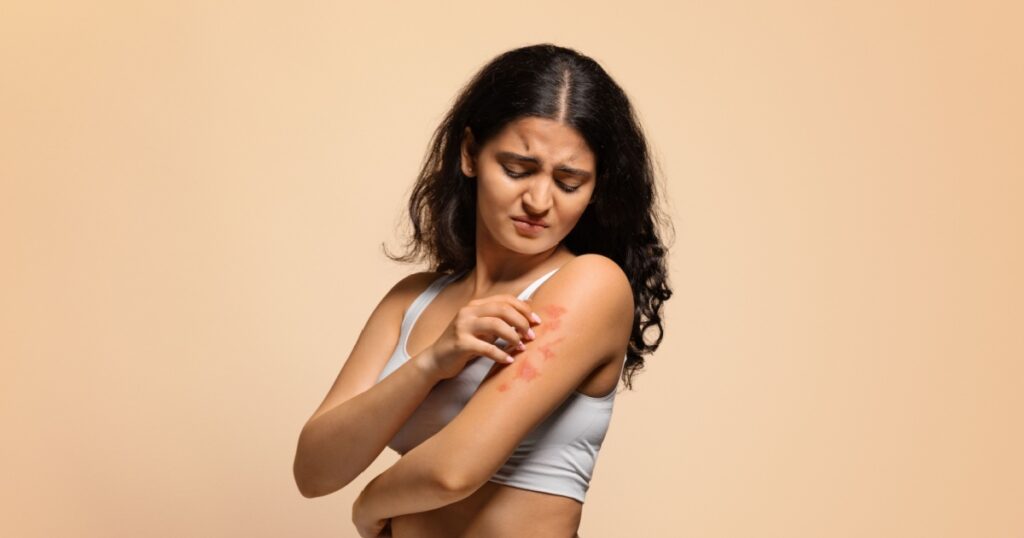
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that leads to the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, silvery scales and itchy, dry, red patches. Treatment for psoriasis typically involves topical medications, phototherapy, and in severe cases, systemic medications to reduce inflammation and slow the excessive skin cell growth. (3)
3. Acne
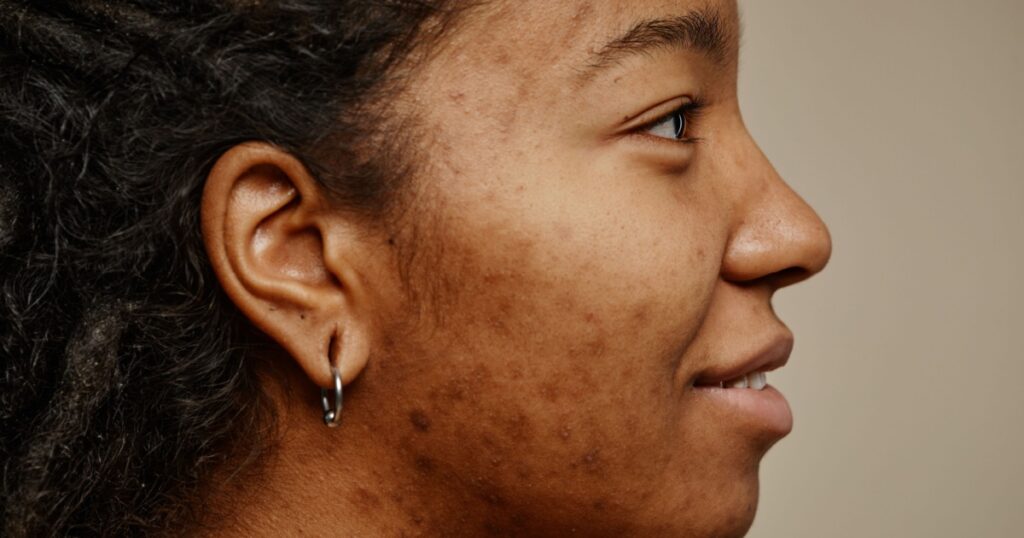
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. While it is often associated with hormonal changes during puberty, it can also affect adults. Treatment options for acne can include topical creams, oral medications, and, in some cases, procedures such as chemical peels or laser therapy. (4)
4. Vitiligo
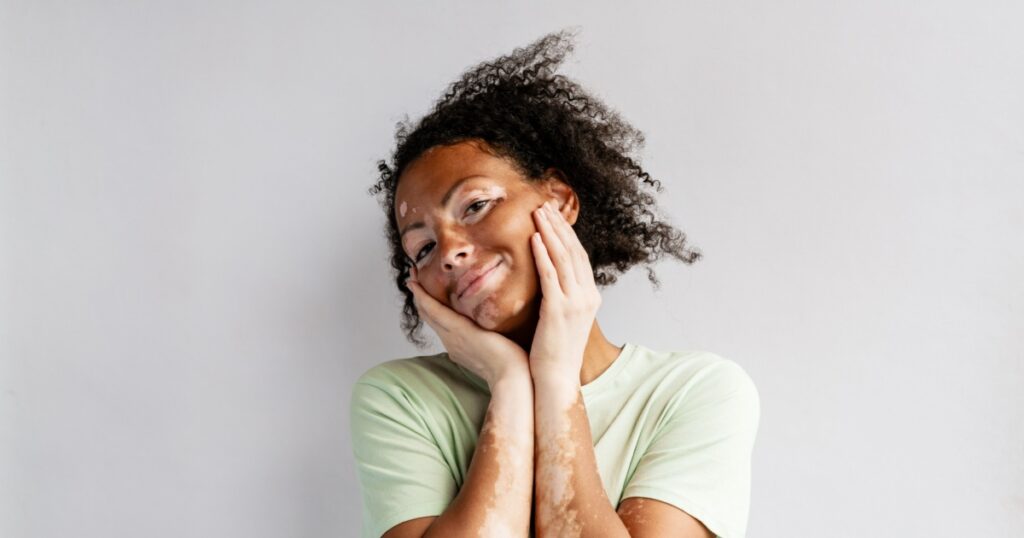

Vitiligo is a skin disorder that causes the loss of skin color in blotches. The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to autoimmune, genetic, and environmental factors. While there is no cure for vitiligo, treatment options such as topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, and depigmentation can help manage its symptoms. (5)
5. Rosacea
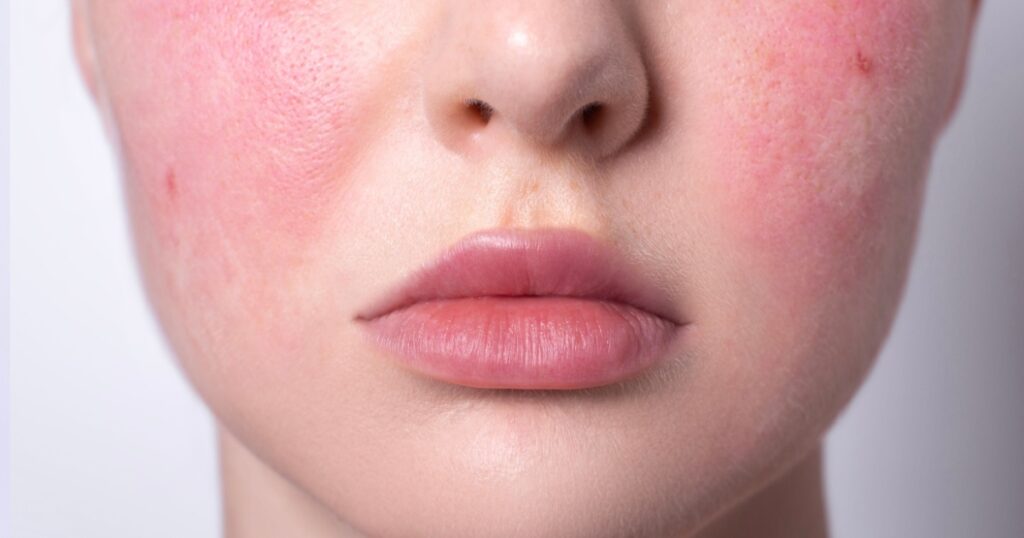
Rosacea is a common skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and pimple-like bumps. Triggers for rosacea can vary, and management often involves identifying and avoiding these triggers, along with the use of topical and oral medications to reduce inflammation. (6)
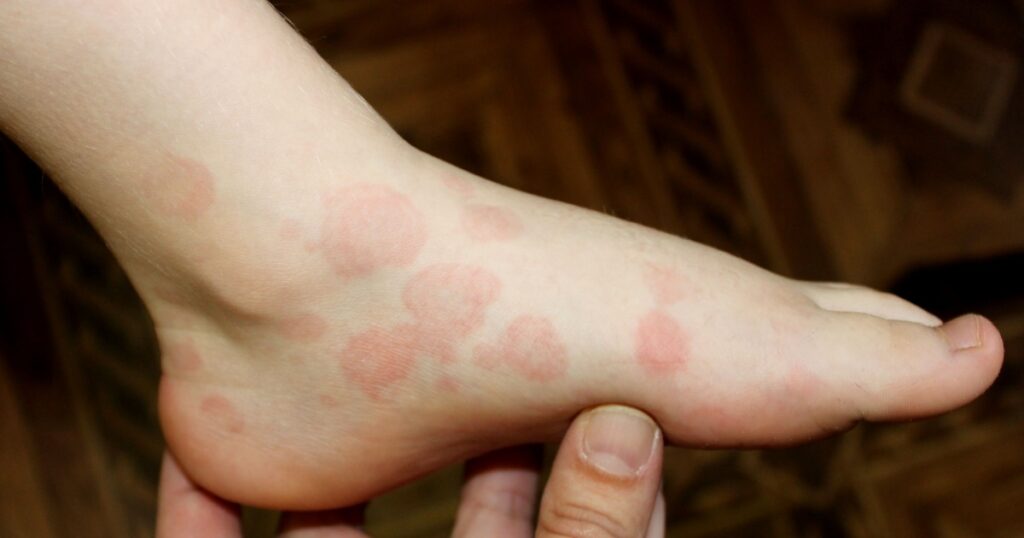
6. Hives
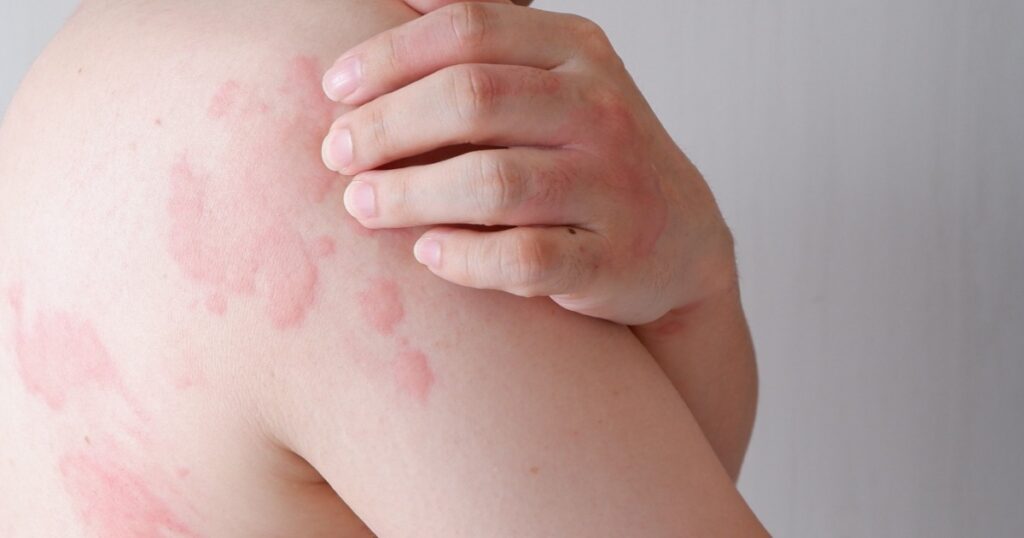
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, red, itchy welts on the skin that can be triggered by various factors such as allergic reactions, stress, or infections. Antihistamines are commonly used to alleviate the symptoms of hives while identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial in preventing recurrence. (7)
7. Skin Cancer
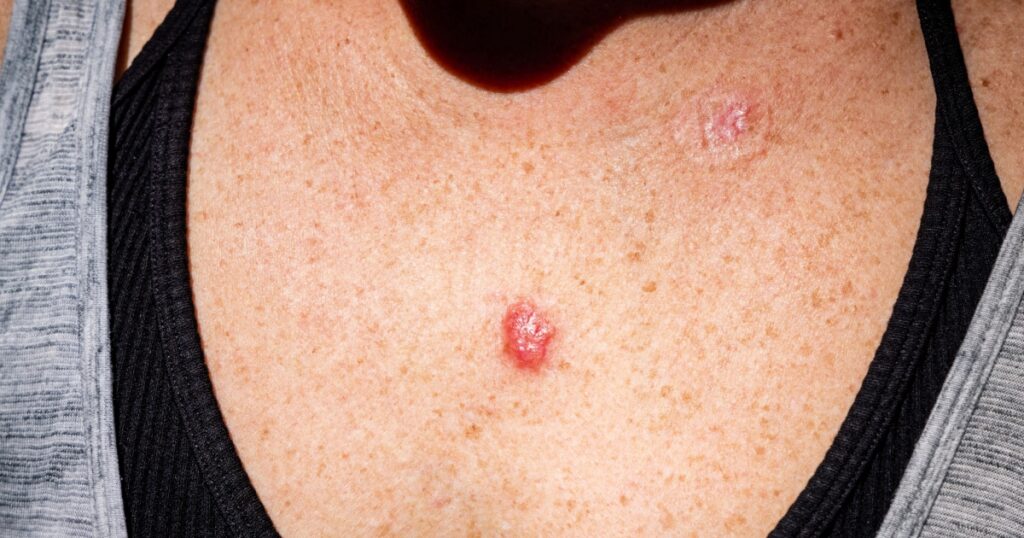
Skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, can manifest as changes in the skin such as new moles, growths, or changes in existing moles. Early detection and treatment are essential in managing skin cancer, often involving surgical removal of the affected area and, in some cases, additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. (8)
8. Shingles
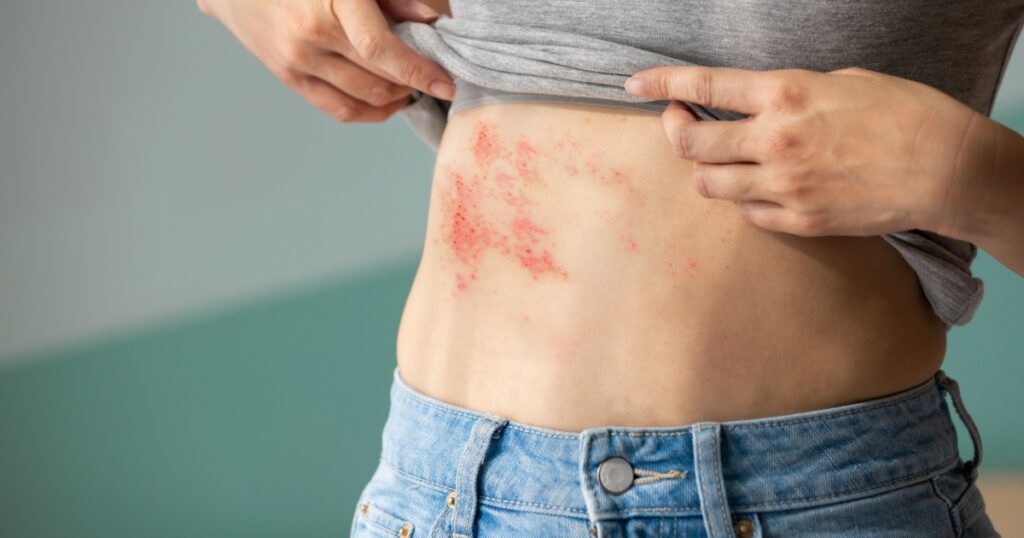

Shingles, caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, results in a painful rash with blisters. Antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of shingles, while pain management strategies may also be necessary to alleviate discomfort. (9)
9. Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of rare, chronic diseases that result in the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. Treatment for scleroderma focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications, often involving a multidisciplinary approach with medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. (10)
10. Erythema Multiforme